Data Integration and Analytics Model
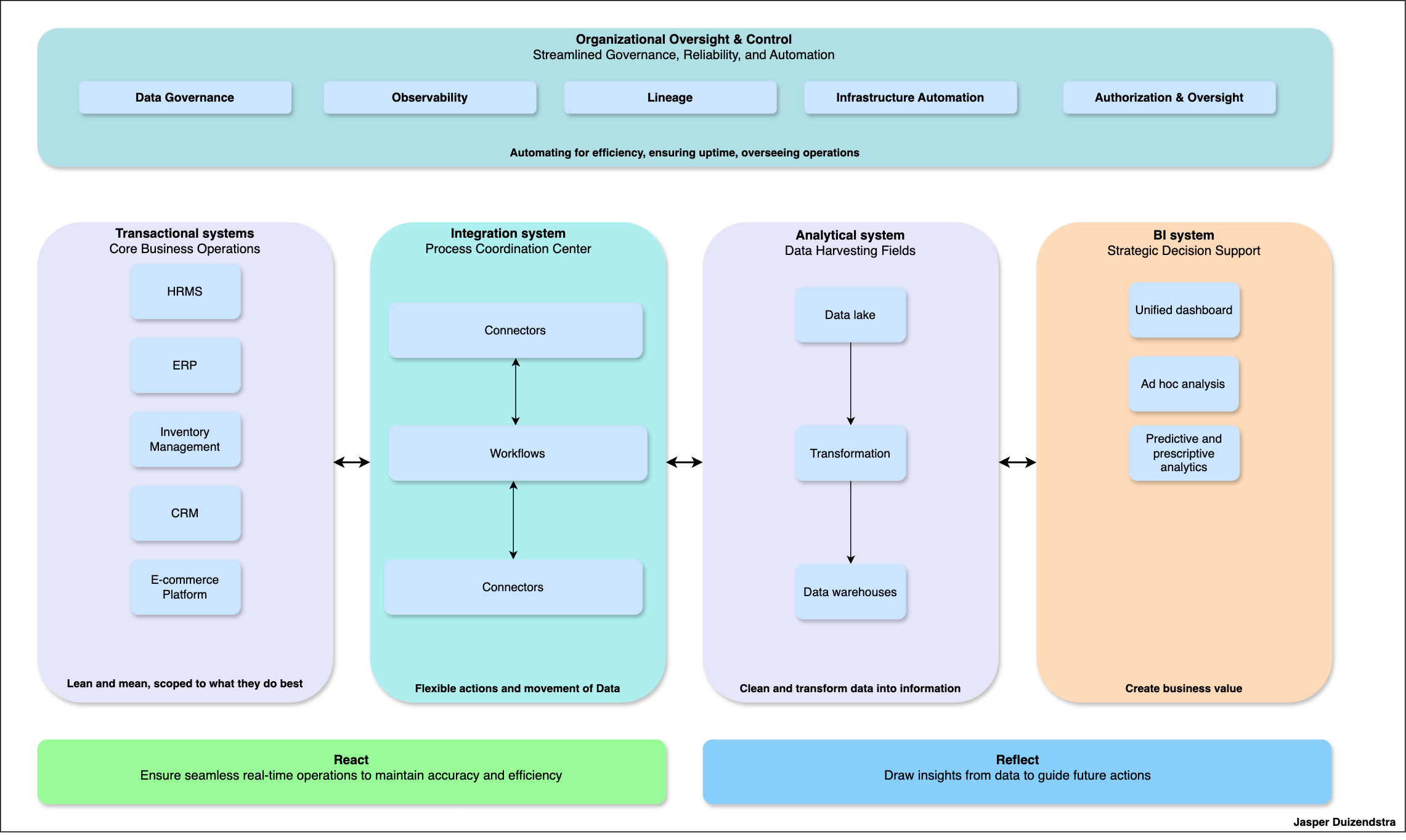
Core Components of the Data Model
-
Transactional Systems: These systems handle core business operations, including HRMS, ERP, Inventory Management, CRM, and E-commerce platforms. The focus here is on lean and mean operations, scoped precisely to what they do best.
-
Integration System: Acting as the process coordination center, this layer facilitates the flexible movement of data through connectors and workflows, ensuring seamless interactions between transactional and analytical systems.
-
Analytical System: This system is the data harvesting field where raw data is cleaned, transformed, and stored in data warehouses after passing through the data lake. It turns data into actionable information.
-
BI System: Serving as the strategic decision support layer, this system generates business value through unified dashboards, ad hoc analysis, and predictive/prescriptive analytics.
Organizational Oversight & Control
The overarching layer ensures streamlined governance, reliability, and automation. Key areas include data governance, observability, lineage, infrastructure automation, and authorization & oversight. This ensures that all systems work efficiently while maintaining high standards of data integrity and accessibility.
Practical Applications
- React: The integration system allows for real-time operations, maintaining accuracy and efficiency across all transactional systems.
- Reflect: The analytical and BI systems draw insights from the data, guiding future actions and creating significant business value.
Visual Model
Below is the visual representation of this data model:
By applying this model, organizations can ensure that their data operations are not only efficient but also provide valuable insights that drive strategic decisions.